While about 300 SNRs are known in our Galaxy today, the number of SNRs predicted by stellar evolution models is 4–6 times higher, indicating an observational bias due to selection effects. Using eRASS we will search for these missing SNRs in the X-ray band and study the spectrum and morphology of the 70 highly significant SNR candidates of the ROSAT all-sky survey. We will perform a systematic study of the entire population of SNRs in our Milky Way and the Magellanic Clouds and investigate environmental effects on the emission as well as on the evolution of SNRs. We expect to detect previously unknown, highly absorbed extended X-ray SNRs or those with X-ray synchrotron emission. The X-ray emission of the latter will reveal the properties of the shock and the magnetic fields, which are crucial for the understanding of the acceleration of cosmic rays in SNR shocks.
In the first funding period of eRO-STEP (2021-2024), we have started searching for missing SNRs in the Milky Way in the X-ray band and studying the highly significant SNR candidates of the ROSAT all-sky survey and the H.E.S.S. Galactic plane survey, using eROSITA All-Sky Survey (eRASS) data. In the second funding period, we are continuing the systematic study of the population of SNRs in our Milky Way and the Magellanic Clouds, by complementing the eRASS data with data of the new ASKAP EMU/POSSUM survey and the MeerKAT Galatic plane radio survey. eRASS results are also being combined with gamma-ray data to study particle acceleration in selected SNRs.
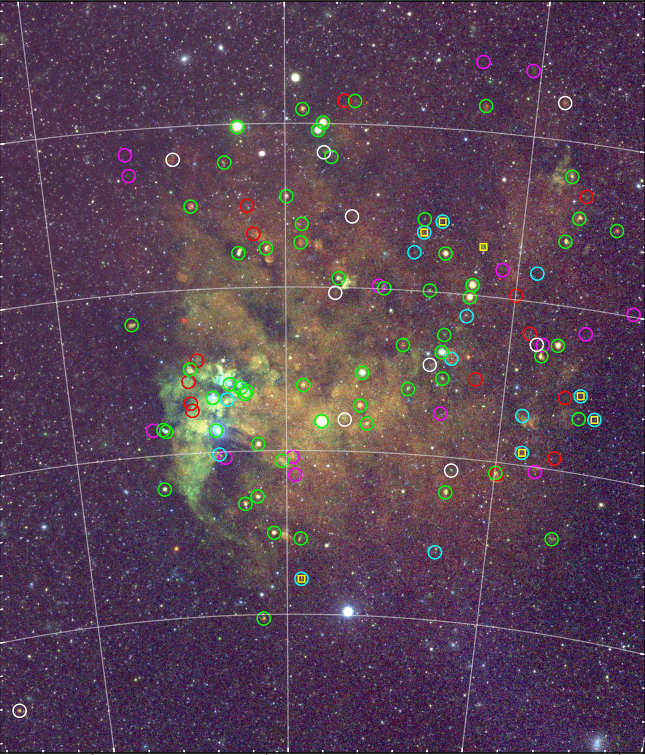
eRASS:4 mosaic image of the Large Magellanic Cloud, with indicated positions of known SNRs green & yellow), SNR candidates (cyan, red & magenta), and newly found potential SNRs (white). Credit: Zangrandi et al. (2024), submitted 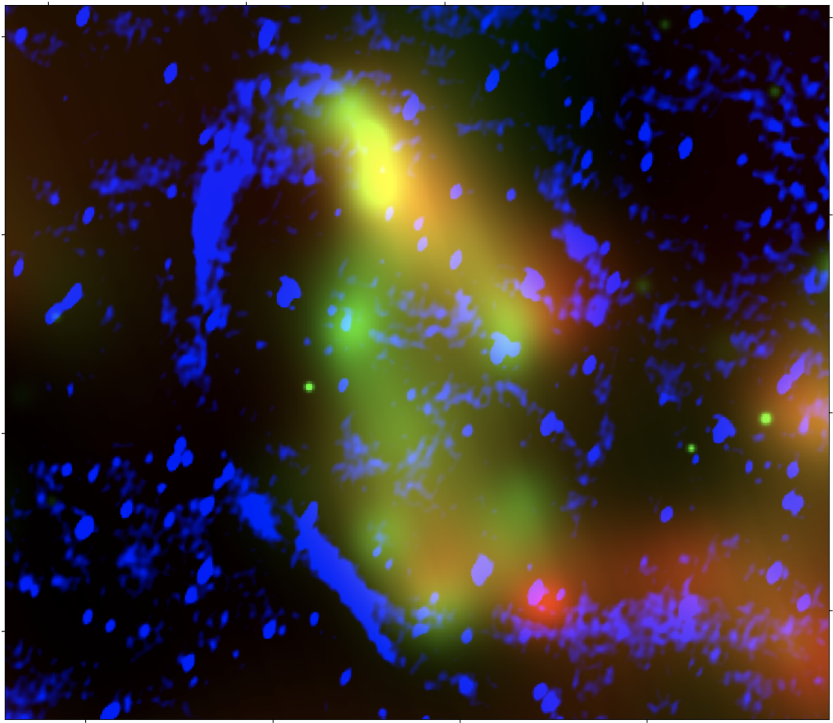
Composite eROSITA X-ray (red, green) and MWA radio (blue) image of the newly confirmed SNR G321.3-3.9.
Credit: Mantovanini et al. (2024)






